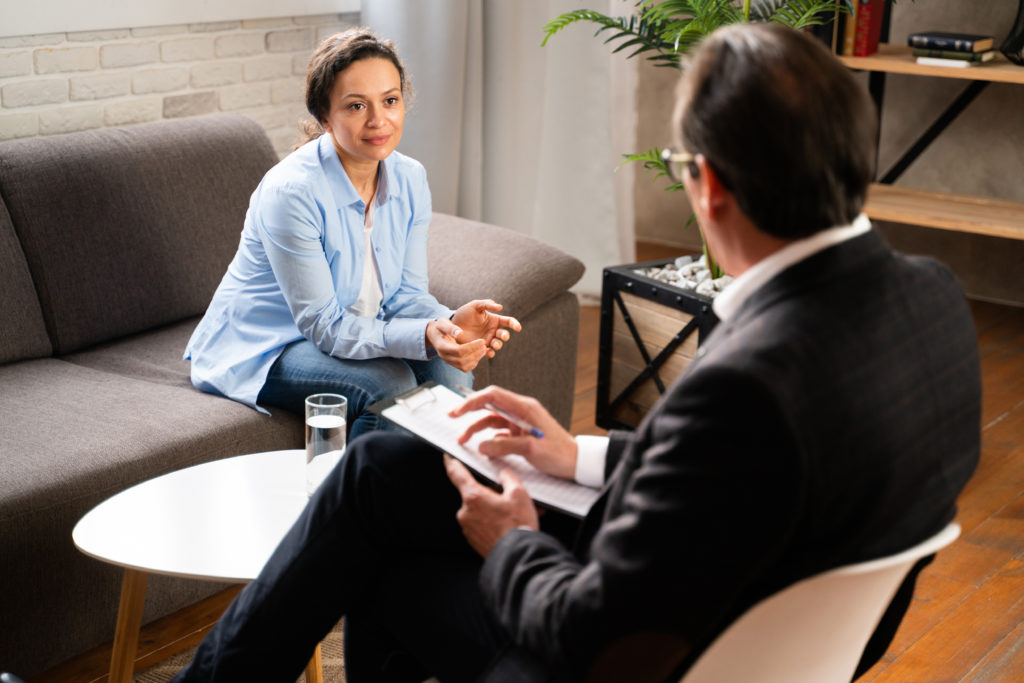
Therapy serves as a vital resource for individuals seeking support and healing in the realm of mental health. But who are the primary users of therapy, and what factors influence their engagement with mental health treatment? By examining demographic trends and societal shifts, we can gain valuable insights into the populations that utilize therapy the most and the reasons behind their seeking support.
Understanding Demographic Trends:
Gender Disparities:
Research suggests that women are more likely than men to seek therapy. Societal expectations around emotional expression and coping mechanisms may contribute to this disparity, with women often feeling more comfortable seeking help for emotional issues. However, efforts to destigmatize mental health treatment are gradually narrowing this gender gap, encouraging men to prioritize their mental well-being.
While therapy is utilized across all age groups, certain demographic segments are more likely to seek treatment at different stages of life. Young adults, particularly those in their late teens and early twenties, often turn to therapy to navigate transitions, identity exploration, and academic or career-related stressors. In contrast, older adults may seek therapy to address issues related to aging, grief, and life transitions, such as retirement or loss of independence.
Ethnic and Cultural Factors:
Cultural beliefs, values, and stigma surrounding mental health vary across ethnic and cultural groups, influencing help-seeking behaviors. Historically marginalized communities, including Black, Indigenous, and People of Color (BIPOC), may face barriers to accessing mental health care, including systemic inequities, cultural stigma, and limited availability of culturally competent providers. Efforts to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion in mental health care are essential for ensuring that all individuals have access to culturally sensitive and affirming treatment.
Socioeconomic Status:
Socioeconomic factors, such as income, education, and access to health insurance, play a significant role in determining who has access to therapy. Individuals with higher socioeconomic status are more likely to have the financial resources and insurance coverage needed to afford therapy services. In contrast, those facing financial hardship or lacking adequate insurance may encounter barriers to accessing care, exacerbating disparities in mental health treatment.
Intersectionality:
It’s important to recognize that individuals occupy multiple intersecting identities, such as race, gender, sexuality, and disability, which shape their experiences and access to therapy. Intersectionality highlights the complexity of identity and the ways in which systems of power and privilege intersect to influence mental health outcomes and treatment utilization

While therapy is a valuable resource for individuals across diverse demographic groups, disparities in access and utilization persist. Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach that considers the intersecting influences of gender, age, ethnicity, culture, socioeconomic status, and other factors. By promoting inclusivity, accessibility, and culturally responsive care, we can ensure that therapy is available to all who seek support on their journey toward healing and well-being.
Check out Ocean Studio 360 Blog today to learn more about the latest web development trends and how they can benefit your online presence and business growth.
Visit our website today to learn more about therapy services.